It’s only normal for any expectant mother to have lots of different questions about their pregnancy. One common question is how to tell if you’re expecting twins. As multiple or twin pregnancies are also a little different from a singleton pregnancy, it’s only natural for pregnant women to want to have as much information as possible at their fingertips.
Since hCG levels and twins have a connection, it’s not too surprising that so many women who get a positive pregnancy test ask whether their hCG level will indicate if they are having multiples or not. In most cases, it’s a fairly good indicator, but it’s not foolproof, so don’t make any major decisions based solely on a high hCG result.
With this in mind, we take a closer look at the connection between twins and hCG so that you can have more of the information you need at your disposal.
- What Is the Link Between hCG Levels and Twins?
- How are hCG Levels Different in Twin Pregnancies?
- Why Are hCG Levels Higher in Twin Pregnancies?
- When Is hCG Produced?
- How Often Will hCG Multiply?
- Why Are hCG Level Tests Carried Out?
- Are hCG Tests Painful?
- What Might Affect My hCG Level?
- Does a High hCG Level Mean I’m Expecting Twins?
What Is the Link Between hCG Levels and Twins?
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (also known as hCG) is the hormone that helps in the detection of pregnancy. If you’re expecting one baby, the level of hCG in your body will range between 70 and 750 mlU/ml (or milli international units per millilite, a unit used for measuring hormones).
If you’re expecting twins, you’ll typically find that the level of hCG in your body will be higher at an earlier stage of pregnancy. Typically, the hCG level for twins will be around 30-50% higher when compared with a single pregnancy at somewhere about 200 – 1750 mlU/ml. hCG levels may double every two or three days when you’re in the early stages of pregnancy.
A blood test will show the best result if taken around 7-8 days following ovulation. The majority of home pregnancy tests will be able to detect if you’re pregnant around four or five days before your period is due to arrive.
How are hCG Levels Different in Twin Pregnancies?
When compared with single pregnancies, hCG levels are very different in cases of twin pregnancies. See the comparison below:
| Days from last menstrual period | hCG range in single pregnancies | hCG range in twin pregnancies |
| 28 | 9.4 – 120 | 9.5 – 120 |
| 33 | 300 – 600 | 200 – 1800 |
| 36 | 1200 – 1800 | 2400 – 36000 |
| 40 | 2400 – 4800 | 8700 – 180000 |
| 45 | 12000 – 60000 | 72000 – 180000 |
| 70 | 96000 – 144000 | 348000 – 480000 |
Why Are hCG Levels Higher in Twin Pregnancies?
Your body cannot produce hCG. Instead, it is made by the developing baby itself. Every developing baby will secrete some hCG, and this is why the levels are doubled in twin pregnancies. The hormones work together to ensure the uterus lining is thick enough to support the growing pregnancy.
The hormone which stimulates the womb to get ready for pregnancy is known as progesterone. Made by the corpus luteum endocrine gland inside the ovary, this hormone must be kept at the correct balance by hCG until such time as the placenta is sufficiently developed to begin producing progesterone on its own.
If you’re pregnant with twins, the level of hCG will increase dramatically and this will it quicker to detect hCG in urine and blood tests. The level will double around every 48-72 hours.

There is one negative side effect of a high level of hCG when you’re expecting twins – it may cause increased morning sickness in the early weeks of pregnancy, which leads to increased vomiting and nausea.
When Is hCG Produced?
Immediately after the fertilized egg implants in the uterus, hCG begins to be made in the placenta. In the early stage of pregnancy, it may be found in the woman’s urine or blood by carrying out an hCG test. As the level of the hormone fluctuates before your period is due, it’s always best to do a test after missing a period.
In some cases, a high level of hCG together with symptoms of pregnancy may indicate a molar pregnancy. This is a condition in which the placenta doesn’t grow properly when the egg and sperm meet during fertilization. The sperm fertilizes an empty egg, which leads to a growth of placental tissue, but no baby.
When this occurs, it’s called a complete molar pregnancy, but there is another form of this condition known as a partial molar pregnancy in which the fetal mass contains both abnormal cells, which contain serious birth defects, and an embryo. The embryo ends up consumed by the mass of abnormal cells.
An elevated level of hCG may also occur because of a rare type of cancer known as a gestational trophoblastic tumor. When given early treatment, this cancer can be easily cured.
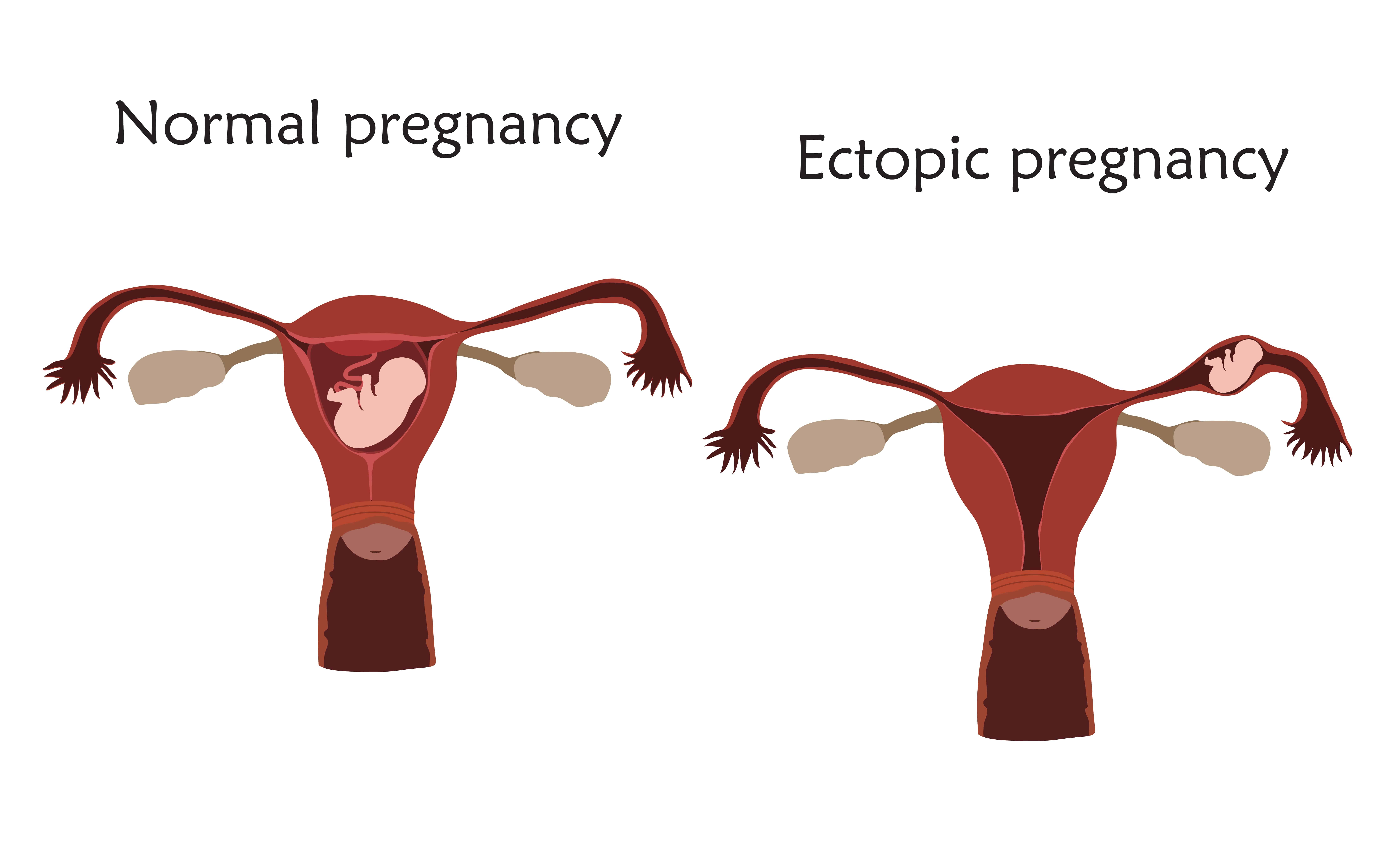
One further reason for a high level of hCG is due to an ectopic pregnancy in which the embryo is growing out of the uterus, usually in one of the fallopian tubes. This requires immediate treatment as the fallopian tube isn’t designed for holding growing embryos.
These days, hCG is also often injected into women who struggle with infertility as it helps to boost their progesterone levels and improve their chance of getting pregnant.
How Often Will hCG Multiply?
When your embryo continues to grow and develop in your uterus into a fetus, the amount of hCG that is released will increase rapidly, approximately doubling every 2 to 3 days.
The first level of hCG determine by testing will be said to be your baseline level. Doctors use this level to work out how well your pregnancy is progressing using the “doubling time” concept that states hCG levels increase by double in early pregnancy.
When your pregnancy is more advanced, hCG release will slow down considerably. It takes between 72 and 96 hours for hCG to develop if it’s valued at 1200-6000 mlU/ml. Once hCG values have reached more than 6000 mIU/ml, it will take 4 days or longer to double.
If your hCG level has reached between 1000 and 2000 mlU/ml, you should be able to see your baby’s gestational sac by using a transvaginal ultrasound. Once the level of hCG has gone about 6000 mlU/ml, though, the growth will slow down and will remain consistent across the remainder of your pregnancy. These hCG blood tests allow doctors to monitor a pregnancy’s development carefully.
After the level of hCG in a woman’s body has reached more than 6000 mlU/ml, it’s possible to carry out a sonogram to give a clear depiction of the pregnancy.
If there’s any doubt over the level of hCG in the woman’s system, ultrasound screenings are often one of the first tests carried out. They can help to ascertain and assess the growth and age of the fetus since the level of hCG in the blood can vary in different women. Transvaginal scans are more common in the early stages of pregnancy since they have a higher level of accuracy than abdominal scans at this point.
If the level of hCG is extremely low, this may be an indicator of ectopic pregnancy, a blighted ovum or a miscarriage, and therefore, regular monitoring is required to diagnose the problem. Yet, even if a woman has a low hCG level, it’s still possible for her to give birth to a healthy baby. In this scenario, the result from ultrasound scans taken after 5 or 6 weeks into the pregnancy will be more reliable than the figures taken from an hCG test result.
Why Are hCG Level Tests Carried Out?
There are several reasons for performing an hCG level test. They include:
- To confirm that a woman is pregnant
- To identify or diagnose abnormalities like ectopic pregnancies
- To diagnose potential miscarriages
- To determine PAPP-A levels in the bloodstream. If they are low, it indicates an increased risk of Downs Syndrome.
Are hCG Tests Painful?
Two tests can be used to identify the level of hCG in your system – a blood test or a urine test. Apart from pinching when the needle is inserted into the vein, blood tests aren’t especially painful.
Urine tests can be done at home, and they have an accuracy rate of around 97% as long as they are carried out correctly. These tests are sensitive to the level of hCG in your urine and will change color in the case of a positive test.
If you’re taking a urine test at home, you can make sure you’re properly prepared by:
- Reading all of the instructions provided with the test kit carefully so you know how it’ll work.
- Checking the kit’s expiry date as this may also impact on the test result.
- Not consuming a lot of water before you take the test since this dilutes your urine’s hCG levels.
- Taking the test as soon as you get up before you eat or drink anything for the most accurate result.
- Taking the test a minimum of 7 to 14 days after missing a period to get the most accurate result.
Although urine hCG tests can determine whether or not hCG is present in your system and, therefore, whether or not you are pregnant, they cannot tell you how much hCG is present.
Blood tests are, therefore, the best way of identifying not only hCG’s presence in your body but also the exact amount present. This type of test can be used for other purposes too, including monitoring pregnancies, diagnosing ectopic pregnancies, determining progesterone levels, working out the risk of miscarriage or diagnosing cancer.
People who suffer from a bleeding disorder may experience issues after having a blood test carried out. They may experience swelling in the veins following the taking of blood samples, but this is very rare and, in the majority of cases, there are no problems associated with hCG blood tests.
What Might Affect My hCG Level?
There are several things that can affect your hCG level. These include:
- A multiple pregnancy – every baby growing in the mother’s uterus will release an amount of hCG and this will increase the hCG level overall in her body. This is why women who are expected twins or multiples will have an hCG level that is double or even triple that of a woman who has a single pregnancy.
- Genetic defects – a very high level of hCG could be due to some genetic problems that occurred during the fertilization process. It could suggest the baby has Downs Syndrome. Molar pregnancies could also be a possibility. These occur if the placenta becomes an abnormal cell mass and causes the baby’s death inside the uterus.
- Genetic complications – a low hCG level could be occurring because of a genetic complication that could cause a miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy. The pregnancy may be terminated or complicated because of this.
- Cancer – sometimes, cancer growing in the large intestine, pancreas, lungs, liver, stomach or uterus may raise the hCG level.
- Influencing factors – if you have taken a pregnancy test too early in your pregnancy or too late in the day when your urine has been diluted, you may get a false negative result on an hCG test. The most accurate result can be achieved by testing your urine when you first get up before eating or drinking.
- Infertility treatment – women struggling with infertility are often injected with hCG to boost their progesterone level and this will increase the amount of hCG in their body.
Does a High hCG Level Mean I’m Expecting Twins?
Although having a higher than expected level of hCG in your system could indicate that you are expecting twins, this isn’t necessarily the case. hCG levels vary between women and even between pregnancies. While hCG levels may be a key factor in spotting that you are expecting twins, it isn’t the only determinant indicating a twin pregnancy since there are other conditions that can cause hCG levels to be high.
